- How to Know When It’s Time to Replace Your Hearing Aids - July 8, 2024
- Hearing Aid Repair and Cleaning Best Practices - June 24, 2024
- The Lifelong Benefits of Early Detection and Addressing Your Hearing Loss - June 10, 2024
Hearing is one of our most vital senses, allowing us to connect with the world around us. However, hearing loss is a common issue that can affect anyone at any age. Understanding what to expect at your hearing exam and comprehending the results is crucial in addressing hearing issues early and effectively. In this article, we will guide you through the hearing exam process, discuss recent advancements in hearing loss prevention, diagnosis, and management, and emphasize the importance of early detection.
The Hearing Exam Process
A hearing exam is a comprehensive evaluation of your auditory system, and it is typically carried out by a licensed audiologist. The purpose of the exam is to determine the state of your hearing and identify any potential issues. Here’s what you can expect during the process:
Case History:
Your audiologist will start by gathering information about your medical history, family history of hearing loss, exposure to loud noises, and any existing health conditions that might impact your hearing.
Otoscopy:
The exam may begin with a visual inspection of your ears using an otoscope. This is to check for any visible abnormalities, such as earwax buildup or infections.
Pure-Tone Audiometry:
This is one of the most crucial aspects of a hearing exam. You will be asked to sit in a soundproof room and wear headphones. Pure-tone audiometry measures your ability to hear sounds at various frequencies and intensities. You’ll respond by indicating when you hear a sound, usually by pressing a button or raising your hand.
Speech Audiometry:
Your audiologist may also assess your ability to understand spoken words. You’ll be asked to repeat words or sentences at different volumes and pitch levels.
Tympanometry:
This test measures the movement of your eardrum in response to changes in air pressure. It helps in evaluating middle ear function and can detect issues like fluid in the middle ear.
Additional Tests:
Depending on your specific case and any initial findings, your audiologist may recommend additional tests, such as otoacoustic emissions (OAE) or auditory brainstem response (ABR) testing.
Understanding the Results
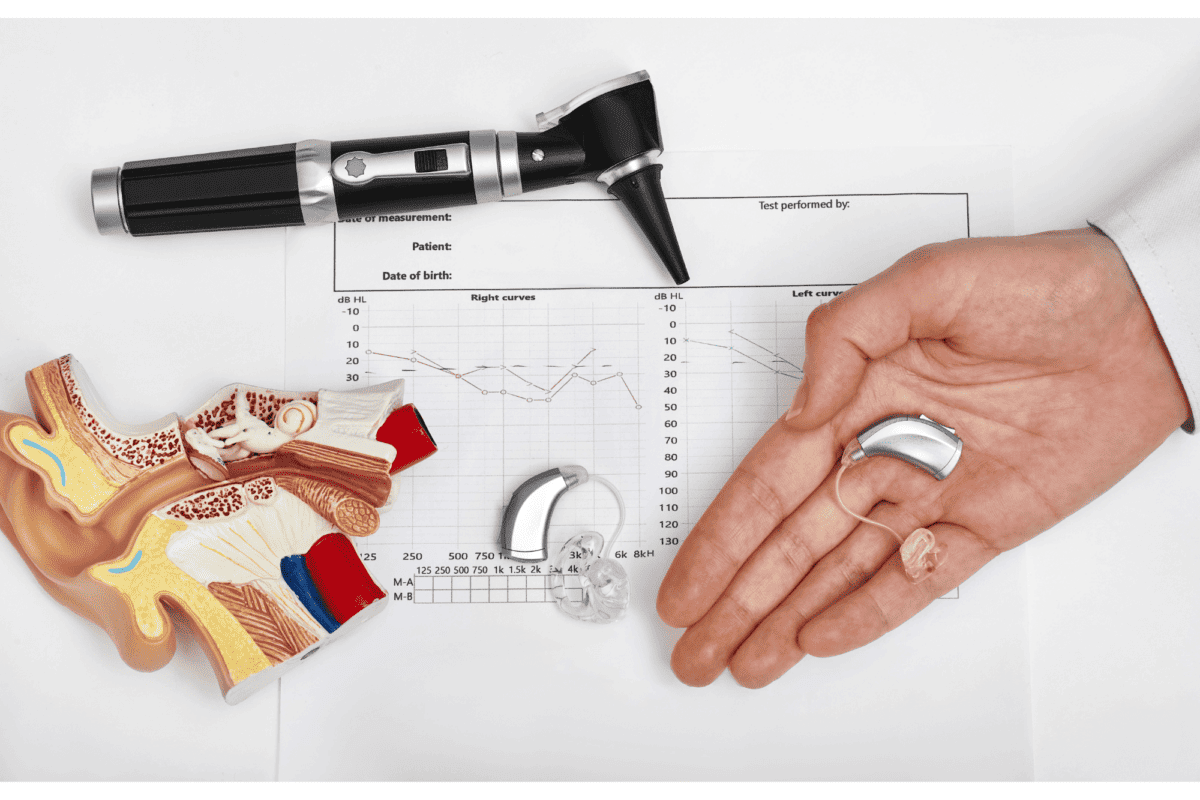
Interpreting the results of your hearing exam is a crucial step in addressing hearing loss. Audiologists use an audiogram, a visual representation of your hearing thresholds, to communicate your results. Here’s how to interpret it:
Audiogram Graph:
An audiogram consists of a graph with two axes. The horizontal axis represents frequency (pitch), ranging from low to high, and the vertical axis represents intensity (loudness), going from soft to loud.
Symbols:
The audiogram will display symbols marking the threshold at which you can hear each frequency. The symbols include O (right ear) and X (left ear). The placement of these symbols on the graph signifies the loudness level at which you can hear specific frequencies. An ‘X’ or ‘O’ above the line indicates the lowest sound you can hear at that frequency, while those below the line indicate sounds that you cannot hear.
Degrees of Hearing Loss:
Based on your audiogram, your audiologist will categorize your hearing loss into degrees, which typically range from normal hearing to profound hearing loss. Understanding these degrees can help you gauge the extent of your hearing loss.
Recent Advancements in Hearing Loss Prevention, Diagnosis, and Management
Prevention:
Hearing loss prevention is increasingly becoming a focus of healthcare. Advancements in personal protective equipment, like high-fidelity earplugs for musicians and noise-canceling headphones, are reducing the risk of noise-induced hearing loss. Additionally, education and awareness about the dangers of prolonged exposure to loud noises are on the rise.
Diagnosis:
Technology has significantly improved the diagnostic capabilities of hearing professionals. Audiologists now use computer-based audiometry for more precise and efficient testing. Furthermore, tele-audiology services have emerged, enabling remote hearing evaluations, which can be particularly beneficial in reaching underserved populations.
Management:
Modern hearing aids have evolved to be discreet, customizable, and incredibly effective. Many are equipped with smartphone connectivity, allowing for personalized sound adjustments and improved user experience. Cochlear implants, a surgically implanted solution for profound hearing loss, have also seen advancements, improving speech recognition and sound clarity for users.
The Importance of Early Detection
Early detection is a cornerstone of effective hearing loss management. Recent research has underlined the importance of identifying and addressing hearing issues as soon as possible. Untreated hearing loss has been linked to various health concerns, including cognitive decline, depression, and social isolation.
Moreover, early intervention allows for a broader range of treatment options. In some cases, simple lifestyle modifications or medical treatment can prevent further deterioration. Even in cases where hearing aids or cochlear implants are necessary, early intervention often leads to better outcomes and improved quality of life.
Future Perspectives
Looking to the future, hearing professionals are continually exploring cutting-edge interventions and technologies. Advances in regenerative medicine hold the promise of repairing damaged hair cells within the inner ear, potentially restoring hearing to those with sensorineural hearing loss.
Additionally, research is ongoing in the fields of gene therapy and pharmacological interventions to prevent and treat hearing loss. These developments may provide new avenues for the prevention and management of hearing impairments.
Your hearing exam is a vital step in understanding and addressing potential hearing loss. By familiarizing yourself with the hearing exam process and interpreting the results, you can take control of your hearing health. Recent advancements in prevention, diagnosis, and management offer hope for a brighter future for those with hearing loss, emphasizing the importance of early detection.
As hearing professionals, our commitment is to provide the best possible care, support, and guidance to those on their journey to better hearing. By staying informed about the latest developments in the field and taking proactive steps toward hearing health, you can look forward to a world of clearer communication and improved quality of life.